 CRM from the Business Strategy Perspective:
CRM from the Business Strategy Perspective:
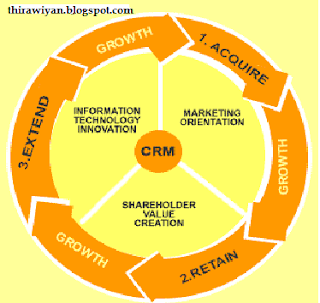
The Business Strategy perspective has most in common with many of the lessons and topics contained on this website, and indeed within the field of marketing itself. The diagram below shows the Marketing Teacher Model of CRM and Business Strategy. Our model contains three key phases - customer acquisition, customer retention and customer extention, and three contextual factors - marketing orientation, value creation and innovatove IT.
We now consider the Business Strategy Perspective on CRM. Here, we propose a model, which is a hybrid, and typical of many of the models and diagrams of CRM that you will find on The Internet and in popular books on the topic of eMarketing/eCommerce. The model has three key phases and three contextual factors:
Three key phases:
- 1. Customer Acquisition.
- 2. Customer Retention.
- 3. Customer Extension.
Three contextual factors:
- 4. Marketing Orientation.
- 5. Value Creation.
- 6. Innovative IT.
1. Customer Acquisition - This is the process of attracting our customer for the first their first purchase. We have acquired our customer.
Growth - Through market orientation, innovative IT and value creation we aim to increase the number of customers that purchase from us for the first time.
2. Customer Retention - Our customer returns to us and buys for a second time. We keep them as a customer. This is most likely to be the purchase of a similar product or service, or the next level of product or service.
Growth - Through market orientation, innovative IT and value creation we aim to increase the number of customers that purchase from us regularly.
3. Customer Extension - Our customers are regularly returning to purchase from us. We introduce products and services to our loyal customers that may not wholly relate to their original purchase. These are additional, supplementary purchases. Of course once our loyal customers have purchased them, our goal is to retain them as customers for the extended products or services.
Growth - Through market orientation, innovative IT and value creation we aim to increase the number of customers that purchase additional or supplementary products and services.
4. Marketing Orientation - means that the wholes organisation is focused upon the needs of customers. Customer needs are addressed by the Three Levels of a Product whereby the organisations not only supplies the actual, tangible product, but also the core product and its benefit, and also the augmented product such as a warranty and customer service. Marketing orientation will focus upon the needs of consumers for all three levels of a product. (N.B. 'market' orientation and 'marketing' orientation are not the same).
5. Value Creation - centers on the generation of shareholder value based upon the satisfaction of customer needs (as with marketing orientation) and the delivery of a sustainable competitive advantage.
6. Innovative IT - is exactly that - Information Technology must be up-to-date. It should be efficient, speedy and focus upon the needs of customers. Whilst IT and/or software are not the entire story for CRM, it is vital to its success. CRM software collects data on consumers and their transactions. Huge databases store data on individuals and groups of individuals. In some ways, CRM means that an organisation is dealing with a segment of one person, since every consumer displays different purchasing habits and preferences. Organizations will track individuals, and try to market products and services to them based upon similar buyer behavior seen in other individuals (e.g. When Amazon tells you those customers that viewed/bought the same product as you, also bought another product).