- Mobilization of Savings: Capital market is an important source for mobilizing idle savings from the economy. It mobilizes funds from people for further investments in the productive channels of an economy. In that sense it activate the ideal monetary resources and puts them in proper investments.
- Capital Formation: Capital market helps in capital formation. Capital formation is net addition to the existing stock of capital in the economy. Through mobilization of ideal resources it generates savings; the mobilized savings are made available to various segments such as agriculture, industry, etc. This helps in increasing capital formation.
- Provision of Investment Avenue: Capital market raises resources for longer periods of time. Thus it provides an investment avenue for people who wish to invest resources for a long period of time. It provides suitable interest rate returns also to investors. Instruments such as bonds, equities, units of mutual funds, insurance policies, etc. definitely provides diverse investment avenue for the public.
- Speed up Economic Growth and Development: Capital market enhances production and productivity in the national economy. As it makes funds available for long period of time, the financial requirements of business houses are met by the capital market. It helps in research and development. This helps in, increasing production and productivity in economy by generation of employment and development of infrastructure.
- Proper Regulation of Funds: Capital markets not only helps in fund mobilization, but it also helps in proper allocation of these resources. It can have regulation over the resources so that it can direct funds in a qualitative manner.
- Service Provision: As an important financial set up capital market provides various types of services. It includes long term and medium term loans to industry, underwriting services, consultancy services, export finance, etc. These services help the manufacturing sector in a large spectrum.
- Continuous Availability of Funds: Capital market is place where the investment avenue is continuously available for long term investment. This is a liquid market as it makes fund available on continues basis. Both buyers and seller can easily buy and sell securities as they are continuously available. Basically capital market transactions are related to the stock exchanges. Thus marketability in the capital market becomes easy.
"Good management consists in showing average people how to do the work of superior people"
Sunday, October 2, 2011
Capital Market role and function
Wednesday, September 7, 2011
Customer Life Time Value:
Comfort Zones:
Monday, September 5, 2011
Types of Customer Loyalty:
Saturday, September 3, 2011
Customer Loyalty
Definition of Loyalty:
Loyalty may be defined as “The biased behavioral response, expressed over time by some decision making unit with respect to one out of a set of processes resulting in brand commitment”.
Loyalty must be seen as “biased repeat purchase behavior” or repeat patronage accompanied by a favorable attitude. Loyalty can originate from factors extrinsic to the relationship such as the market structure in which the relationship exists, but also in intrinsic factors such as relationship strength and handling of critical episodes during the relationship.
Advantages for setting up Loyalty:
1. Building lasting relationships with customers by rewarding them for their patronage.
2. Gathering high profits through extended product usage and cross-selling
3. Gathering customer information
4. Decommodifying brands i.e., differentiating from crowds.
5. Defending market position
6. Planning against competitive activity.
Classification of customers with reference to Loyalty:
There are six classifications of customers in respect of loyalty:
1) Current loyal customers who will continue to use the product or service
2) Current customers who may switch to another brand
3) Occasional customers who would increase consumption of the brand if the incentives were right.
4) Occasional customers who would decrease consumption of the brand if competitor offered the right incentive.
5) Non-users who could become customers.
6) Non- users who could never become customers.
It is important to distinguish between loyalty to the generic product, the brand and particular supplier. Many people drink coffee as beverage. Those who drink considerable quantity of coffee can be described as having a product loyalty. Within the group, there will be some that buy just the cheapest coffee or drink whatever available. They are product loyal but not brand loyal. They are not disloyal as that implies that there has been a loyalty, but they have no loyalty at all to a particular brand. Those who have a particular brand loyalty, they always buy a particular brand or at least a brand from the same product.
Friday, September 2, 2011
Benefits of Customer satisfaction

Thursday, September 1, 2011
Frank (USA, 1867 - 1924) and Lillian (U.S.A, 1878 - 1912)

Customer Satisfaction Process:
Customer Satisfaction
- Core product or service
- Support service and systems
- Technical performance
- Elements of customer interaction
- Affective dimension of services
Henry Lawrence Gantt (USA, 1861 - 1819)

Wednesday, August 31, 2011
Taylor's Scientific Management (USA 1856-1915):
 Started as an apprentice machinist in
Started as an apprentice machinist in - Science, not rule of thumb
- Harmony, not discord
- Co-operation, not individualism
- Maximum output, in place of restricted output
- The development of each man to his greatest efficiency and prosperity.
Tuesday, August 30, 2011
CRM from the Business Strategy Perspective
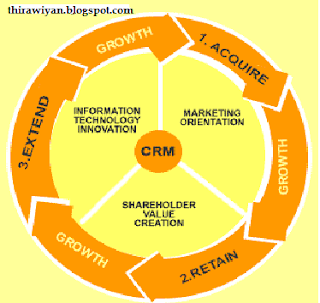 CRM from the Business Strategy Perspective:
CRM from the Business Strategy Perspective: Three key phases:
- 1. Customer Acquisition.
- 2. Customer Retention.
- 3. Customer Extension.
Three contextual factors:
- 4. Marketing Orientation.
- 5. Value Creation.
- 6. Innovative IT.
CRM from the Customer Life Cycle (CLC) Perspective
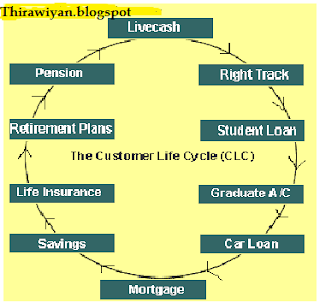
The Customer Life Cycle (CLC) has obvious similarities with the Product Life Cycle (PLC). However, CLC focuses upon the creation of and delivery of lifetime value to the customer i.e. looks at the products or services that customers NEED throughout their lives. It is marketing orientated rather than product orientated, and embodies the marketing concept. Essentially, CLC is a summary of the key stages in a customer's relationship with an organisation. The problem here is that every organisation's product offering is different, which makes it impossible to draw out a single Life Cycle that is the same for every organisation.
Monday, August 29, 2011
CRM Perspectives [Information Technology]
Sunday, August 28, 2011
Needs / objectives of CRM:
Friday, August 26, 2011
Definition of CRM:
Saturday, August 13, 2011
Managerial Skills
discern interrelationships among organizational parts, and understand how the organization fits into the wider context of the industry, community, and world. Conceptual skills, coupled with technical skills, human skills and knowledge base, are important ingredients in organizational performance.
Top management ---------------Concept and design Skills.
Middle management ------------Human Skills.
Supervisor’s --------------------Technical skills.
